
James Fisk

Partner of another infamous robber baron, Jay Gould, the two attempted to corner the gold market in 1869. This corner eventually led to the 1869 Black Friday after the two inflated the price of gold. In addition to cornering the gold market, Fisk was also involved in Erie Railroad War.
Andrew Carnegie

After working in the rail road industry for quite some time, Carnegie quickly became interested in steel. He owned one of the largest steel production companies in the world, but made many mistakes along the way. At one point he attempted to lower the wages of his employees which ended with the Homestead Strike.
John Jacob Astor

Astor left Germany and headed to America in 1793 to start a new life. He immediately entered into the fur trade industry upon arriving in America, and made quite a bit of money doing so. This allowed him to built the American Fur Company, which is now considered the United States first monopoly.
John D. Rockefeller

In 1899 the Rockefeller fortune was work 200 million dollars. After forming the Standard Oil Company with his brother and robber baron Henry Flagler, they grew into a monopoly. They eventually controlled a majority of all U.S. pipelines and refineries.
Henry Huttleston Rogers

Henry Huttleston Rogers is known for creating the machinery that could separate naphtha from crude oil. This invention allowed him come into his wealth after the Rockefeller’s bought his company. He then began working his way up the ranks in the Standard Oil Company.
Cornelius Vanderbilt
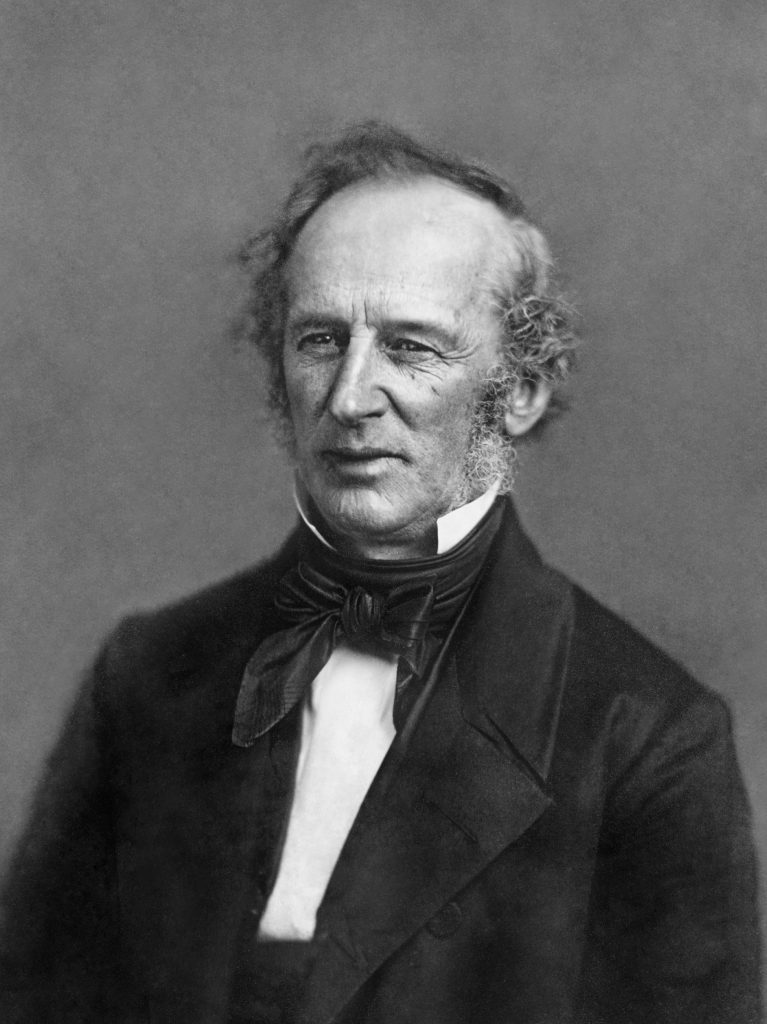
Considered one of America’s first baron robbers, Cornelius made a fortune on his shipping company. He sold all that he had during the way to invest in the railroad because he something that could be a huge success. By the end of the Civil War Cornelius Vanderbilt was worth over 65 million dollars.
J.P. Morgan
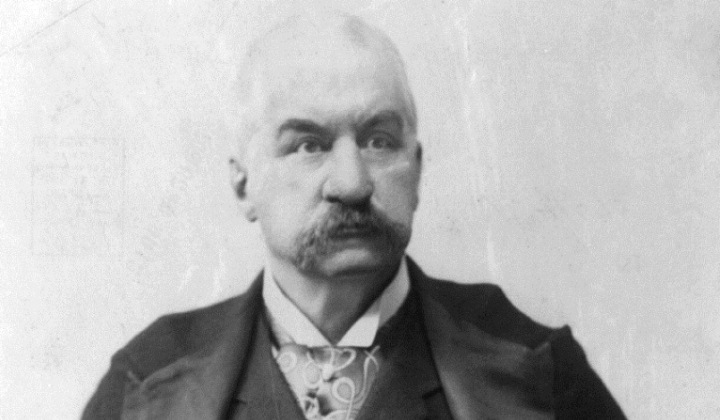
One of the many robber barons to escape serving in the Civil War, he paid 300 dollars for a substitute to fight instead. Morgan is most famous for bailing out the United States by loaning them 60 million dollars.
Jay Cooke
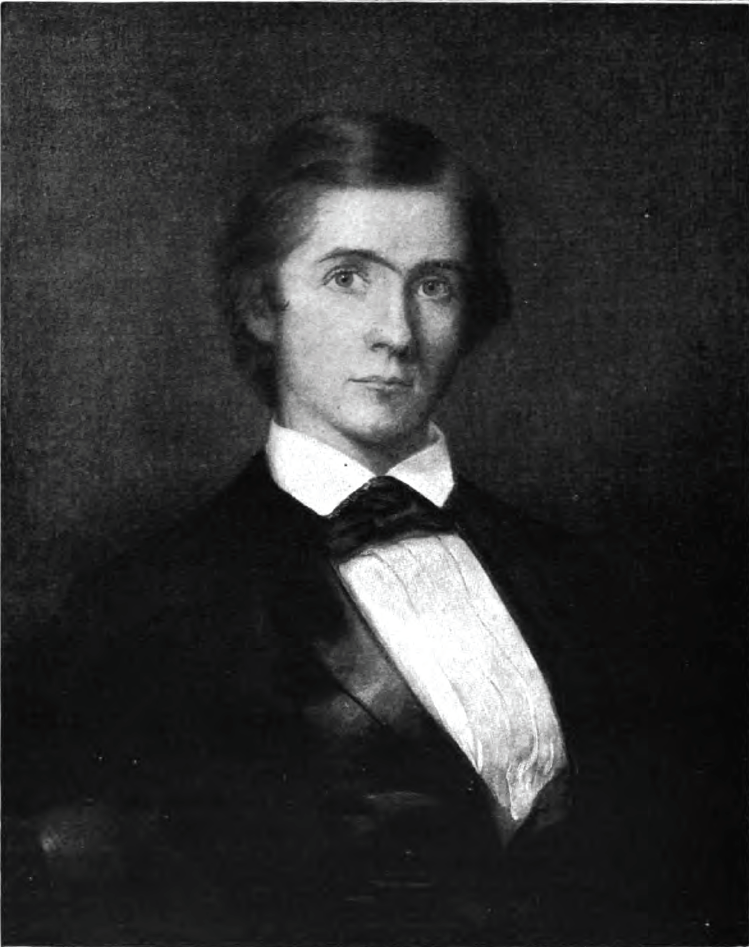

Cooke opened his first bank in 1861 called Cooke & Co. and eventually helped finance the development of railroads after the war. He also loaned the state of Pennsylvania 3 million dollars during the Civil War. After filing for bankruptcy Cooke had to rebuild his fortune and did so by investing in a silver mine in the state of Utah.
Henry Morrison Flagler
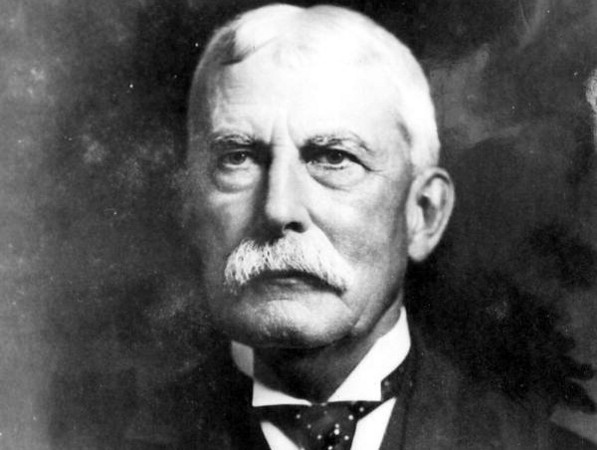

As you already know, Flagler was also apart of the uprising of the Standard Oil Company. He became a huge real estate mogul in Florida, building hotels, fixing railroads, and so on. He is considered the man who built Palm Beach into a tourist destination.
John C. Osgood

Founder of the Fuel and Iron Company, he eventually controlled 69,000 acres of coal land. He also operated 14 mines and is considered the founder of the town Redstone, Colorado.
Andrew Mellon
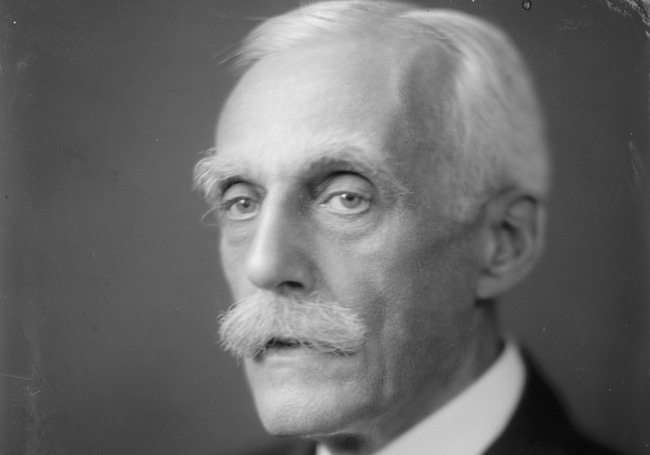

With many titles under his belt Mellon called himself a banker, industrialist, and even a United States Ambassador for the United Kingdom. He helped found the Aluminum Company of America along with many other big companies. In 1921 he was appointed as the Secretary of the Treasury for the United States and served in that position until 1932.
Leland Stanford
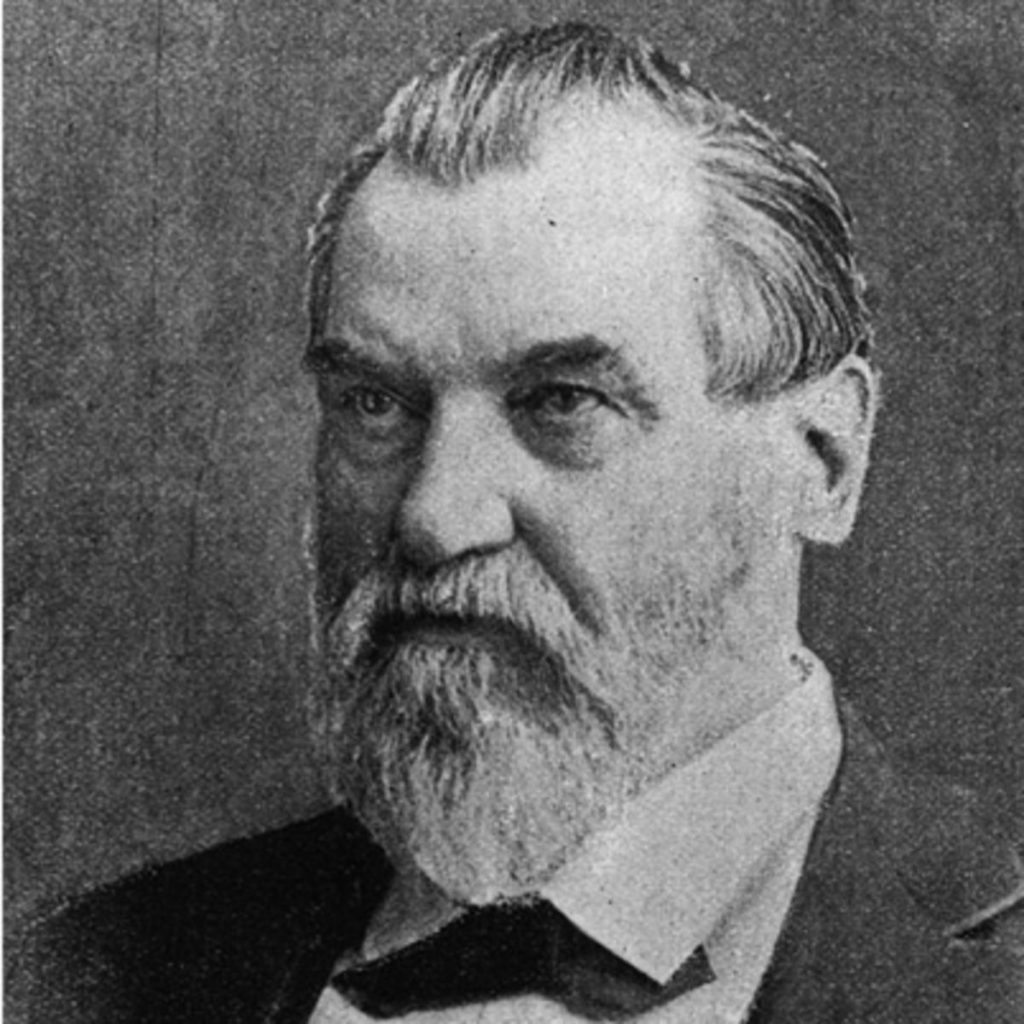
Leland Stanford is the co founder of Stanford University, but has done so much more. He grew his career in the railroad industry alongside Mark Hopkins and Charles Crocker. Stanford also served as a politician for a short time in California in 1861.
Jay Gould

Alongside James Fisk, Gould became involved with the Erie Railroad War. After the war Gould ended up in control of the railroad. Once he gained control over the Erie Railroad he also came into possession of the Union Pacific Railroad in 1873.
Henry Clay Frick
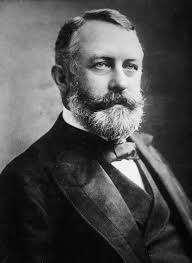
Helping expand Carnegie Steel Company, Henry Clay Frick was a long time partner with Andrew Carnegie. Over the years the two grew apart and their business relationship fell apart.
Charles Crocker

Like many other robber barons on this list, Crocker was involved with the rising railroad companies. He worked with the Central Pacific Railroad company and is known as one of the “Big 4” apart of the project. Eventually he gained control of the Southern Pacific Railroad company and merged the two companies.
James Buchanan Duke

Working in the tobacco and electric power industries, Duke is credited with streamlining the method of hand rolling cigarettes. He eventually controlled 90% of the United States tobacco sales.
Charles M. Schwab

After working for Carnegie Steel, Schwab left and began running Bethlehem Steel. After he took over, Bethlehem Steel became the second largest steel manufacturer in the U.S.
Marshall Field

Field is considered the inventor of the modern day department store. He is the founder of Marshall Field and Company which is a department store based out of Chicago. He has also been credited with allowing customers to return their items they’ve purchased.
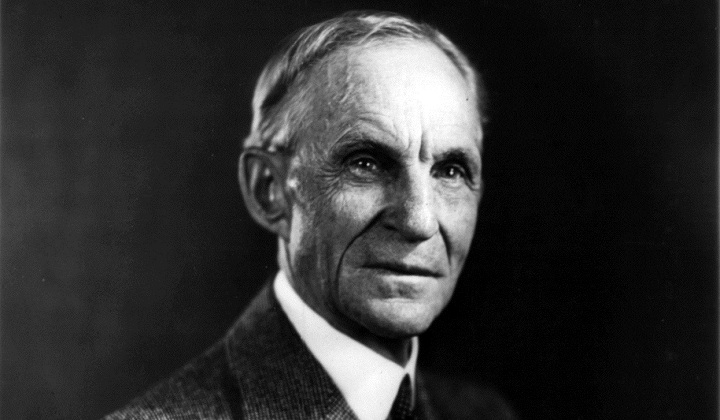
Henry Ford

Founder of the Ford Motor Company, he is responsible for the introduction of the assembly line and mass production. Of course he didn’t invent either of these, but he certainly helped popularize mass production.
Daniel Drew

Drew spent time as a steamship and railroad developer, but eventually turned his career path towards money, literally. He opened a Wall Street Banking firm 1844 called the Drew Robertson Company. He specialized in railroad stock and like many other robber barons lost quite a bit of money during the Panic of 1873.