During the 16th century was when Britain first attempted to establish settlements overseas. By 1670 Britain had colonies in Maryland, New England, and Virginia in America. Britain also had colonies established in Nova Scotia, the Bermudas, Antigua, Barbados, and Honduras. Jamaica was claimed in 1665 by conquest as well.
In the 1670s, the Hudson Bay Company established itself in what we now know as northwestern Canada. Another British company, the East India Company, began to establish trade posts in India beginning in 1600. Through the East India Company, Penang, Singapore, Malacca, and Labuan (also known as the Straits Settlements) became British.
James Island in the Gambia River was established by Britain as its first African settlement in 1661. Sierra Leone later fell under British rule in 1787. In 1806, Britain had settlements in the cape of Good Hope in South Africa. Nearly all settlements and colonies were established by the enterprises of prominent companies. The British Crown had barely participated in the growth of the empire. During the 17th and 18th centuries had control over the colonies and settlements mainly in trade and shipping.
The British and French colonies in North America fought but Britain was later left with Canada. This is because of the Treaty of Paris of 1763 that ended the Seven Years’ war between the French and Native Americans. In India, the French Compagnie des Indes confronted the East India Company. Britain’s military victories against France with the help of Robert Clive and the rulers of Bengal in the 1750s allowed Britain to have India.
In 1783, Britain lost the thirteen colonies in the United States. Five years later Britain had settlements established in Australia. Many loyalists who had been residing in the colonies also moved up to Upper Canada, or what we know as Ontario. This helped the British Empire to grow greatly.
The Treaty of Amiens gave Britain ownership of Trinidad and Ceylon, or Sri Lanka as it is known today, in 1802. France had to give up Tobago, Mauritius, Saint Lucia, and Malta to Britain because of the Treaty of Paris in 1814. Singapore became British in 1819 as well because of Sir Stamford Raffles.
Britain’s empire only grew larger and larger. Settlements were founded in Canada in Alberta, Manitoba, and British Columbia. Through conquests, Britain also came in ownership of more of India. This included the united Provinces of Agra and Oudh, the Central Provinces, East Bengal, and Assam.
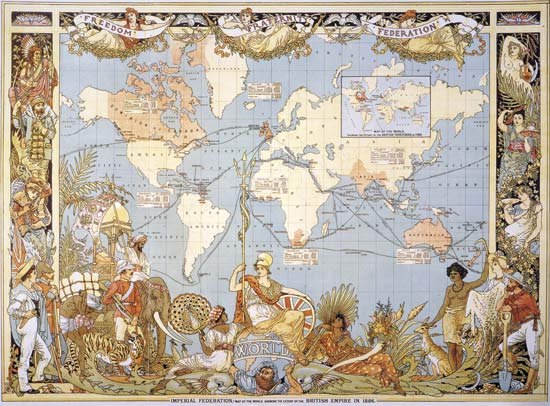
By the 18th century, the empire was at its fullest. New Zealand became British in 1840. Britain continued to extend to Fiji, Tonga, Papua, and several other islands in the pacific ocean. In 1877, the British High Commission for the Western Pacific Islands was created. Though because of the Indian Mutiny in 1857, the East India Company had to give up its governmental role over India to the British crown. In 1886 Burma, or Myanmar, became British. The British also obtained Punjab in 1849 and Balochistān in 1854 through conquest.
The French completed the Suez Canal in 1869, providing a shorter route to India for Britain. It helped Britain expanded its ports to Aden, establish a protectorate in Somaliland (Somalia as we know it), and extended the sheikdoms influence in the Persian Gulf and Cyprus. The straits settlements and the Federated Malay states continued to develop. British influence in the far east continued to grow as well. In the 1880s protectorates were formed over Brunei and Sarawak.
The island of Hong Kong went under British rule in 1841. They operated an “informal empire” in China because of ports and the great trading city of Shanghai. From 1882, Britain ruled Egypt and Sudan from 1899. Thanks to the Royal Niger Company, British influence expanded to Nigeria, too. The Gold Coast, or Ghana as it is known today, and the Gambia soon became British. Kenya and Uganda did as well when the Imperial British East Africa Company began operating there. Southern Rhodesia, or Zimbabwe as we know it, fell under british rule along with Northern Rhodesia, or Zambia, when the British South AFrica Company arrived.
In 1902, the South African War ended. Britain had won and added the Transvaal and the Orange Free Slate to its empire that same year. The Union of South Africa was also created in 1910.
The British Empire amounted for nearly ¼ of the world and over ¼ of the population by the end of the 18th century. In 1839, Lord Durham in Canada had recommended to Britain that instead of British Officials chosen by the government being in control of the colonies, they chose a cabinet of ministers from Canada. Lord Durham’s idea spread widely and was used in the Canadian colonies and later in the Australian Colonies, New Zealand, and South Africa in the Cape Colony and Natal. All nations by that time under British rule were called the British Commonwealth.
In 1914 when Germany went to war with Britain, the British colonies were apart of it. But when World War II began, the nations and colonies under British rule made their own declarations of war. India was granted independence in 1914 and later Burma and Ceylon (now Sri Lanka) were the next year. The gold Coast recover their independence in 1957. Hong Kong was the last colony under British rule. It was finally granted freedom in 1997.